Embryo freezing
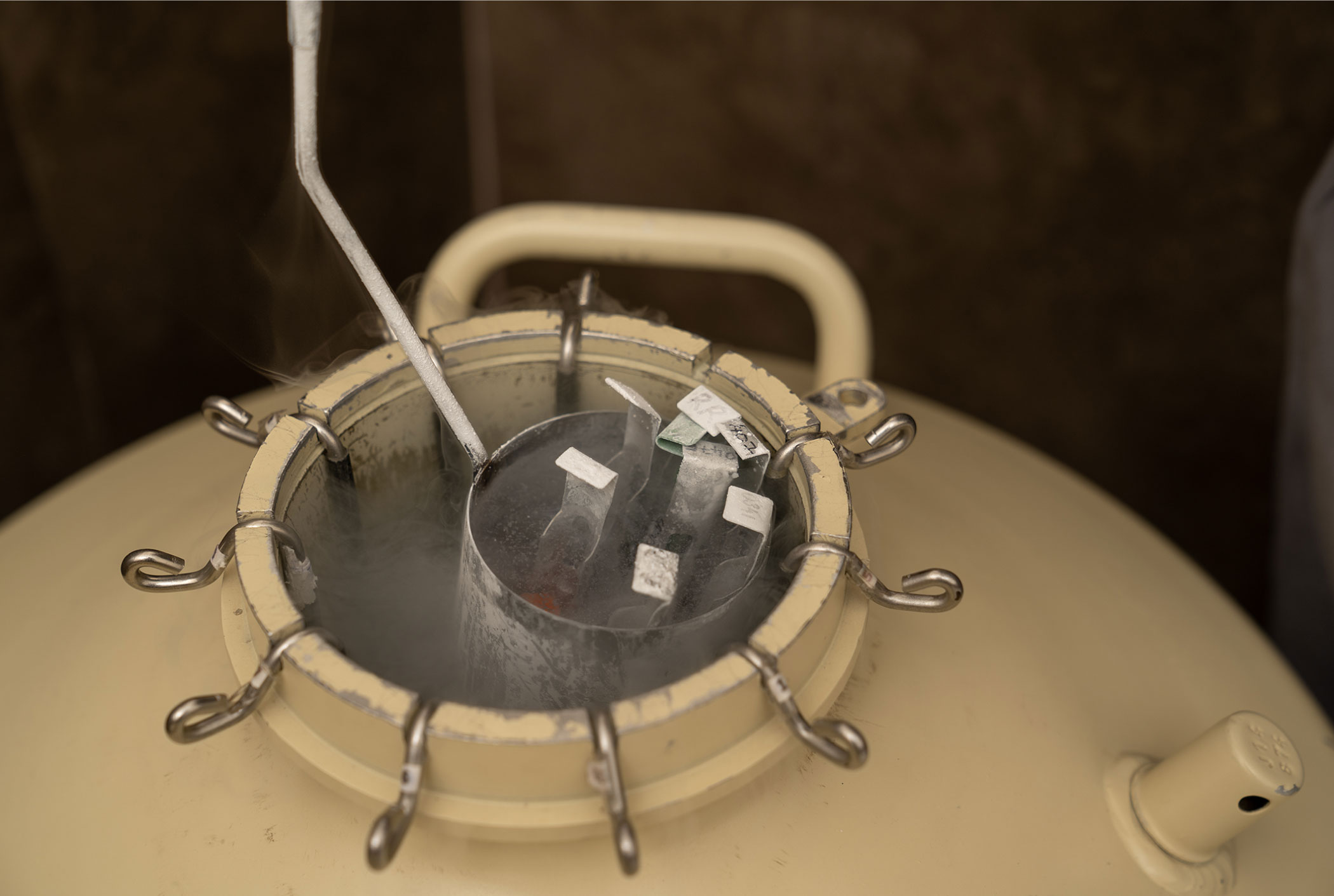
Embryo freezing refers to the process of storing embryos in liquid nitrogen at a low temperature of -196 degree Celsius to be used later in the same patient from whom the embryo was retrieved. During the embryo transfer cycle, the woman will not have to go through superovulation and egg collection all over again. As no hormonal injections are required, the receptivity of the uterus to the embryos is believed to be better. The method is fast, convenient, economical and enjoys a great success rate. These frozen embryos can be stored for as long as is needed – for 25-30 years.
Advantages of embryo freezing
Surplus embryos can be used for treatment later if fresh embryo transfer fails. It also provides an opportunity of trying again without having to undergo ovarian stimulation medication and egg retrieval.
Frozen embryo transfer is more economical compared to the expense of ovarian stimulation medications, blood work, egg retrieval, insemination, embryo culture and ultrasound study. It’s less strenuous and convenient for the patients too as it requires only simple oestrogen supplementation during the proliferative phase of endometrial preparation and progesterone injections to prepare the uterus for embryo implantation.
Freezing embryos reduces the risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (high oestrogen levels, more number of follicles, fluid in the pelvis etc) by maintaining great success rates.
For couples with a risk of passing certain genetic conditions onto their children, we can test the embryos for certain genetic mutations, looking for abnormalities in chromosome number, such as trisomy 21, which causes Down’s syndrome and many others that are likely to result in implantation failure or miscarriage.
Vitrified embryos maintain reproductive potential far into the future, giving our patients time to make a decision to expand their families. Frozen embryo transfer can suspend proverbial biological clock since the embryos thawed maintain the reproductive potential associated with age of the egg at the time it was fertilized.
Freezing is very cost-effective, since transferring frozen-thawed embryos is much less expensive than starting a new cycle. Also, once stored, embryos can be used by the couple during a later treatment cycle, donated to another couple or removed from storage.
Why to go for embryo freezing?
The ability to freeze and thaw embryos successfully is one of the greatest advancements in assisted reproductive technology. There are two techniques of embryo preservation – slow freeze and vitrification. Vitrified embryos have more than 90 per cent freeze-thaw survival rate because of addition of cryoprotectant prior to cooling which acts as antifreeze and prevents crystal formation. Embryos can be frozen at any stage like from Day 2 to Day 5. The technology also has increased implantation rates, increased live birth rates, decreased miscarriage rates, lowered risk of pre-term labour and healthier babies.